The Anatomy of a Leaf
Outer Structure
- midrib - the central rib of a leaf - it is usually continuous with the petiole.
- petiole - a leaf stalk; it attaches the leaf to the plant.
- stipule - the small, paired appendages (sometimes leaf-life) that are found at the base of the petiole of leaves of many flowering plants.
- vein (vascular bundle) or small netted vein - Veins provide support for the leaf and transport both water and minerals (via xylem) and food energy (via phloem) through the leaf and on to the rest of the plant.
- blade - the outline of the leaf
Inner Structure
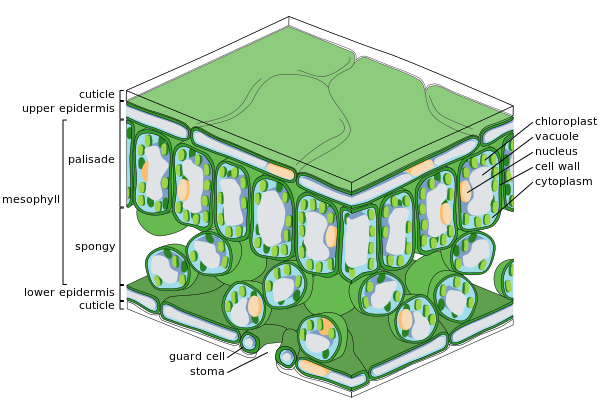
- cuticle - the waxy, water-repelling layer on the outer surface of a leaf that helps keep it from dying out (and protect it from invading bacteria, insects, and fungi). The cuticle is secreted by the epidermis (including the guard cells) and is often thinner on the underside of leaves. The cuticle is generally thicker on plants that live in dry environments.
- epidermis - the protective, outler layer of cells on the surface of a leaf. The guard cells (and stoma) are part of the epidermis. The surface of many leaves is coated with a waxy cuticle which is secreted by the epidermis.
- guard cell - one of a pair of sausage-shaped cells that surround a stoma (a pore in a leaf). Guard cells change shape (as light and humidity change), causing the stoma to open and close.
- mesophyll - the chlorophyll-containing leaf tissue located between the upper and lower epidermis. These cells convert sunlight into usable chemical energy for the plant.
- palisade mesophyll - a layer of elongated cells located under the upper epidermis. These cells contain most of the leaf's chlorophyll, converting sunlight into usable chemical energy for the plant.
- spongy mesophyll - the layer below the palisade mesophyll; it has irregularly-shaped cells with many air spaces between the cells. These cells contain some chlorophyll. The spongy mesophyll cells communicate with the guard cells (stomata), causing them to open or close, depending on the concentration of gases.
- stoma - (plural stomata) a pore (or opening) in a plant's leaves where water vapor and other gases leave and enter the plant. Stomata are formed by two guard cells that regulate the opening and closing of the pore. Generally, many more stomata are on the bottom of a leaf than on the top.
Walang komento:
Mag-post ng isang Komento